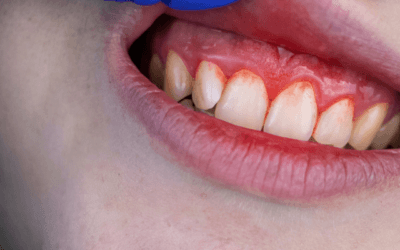
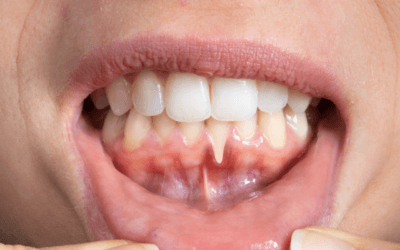
What is Tooth Erosion?
Tooth erosion is the loss of tooth enamel and other tooth structure from frequent exposure to strong acids.
Common Causes Of Tooth Erosion :
- Acidic drinks and foods
- Some medicines
- Stomach acids that regurgitates into the mouth
When Enamel layers become eroded
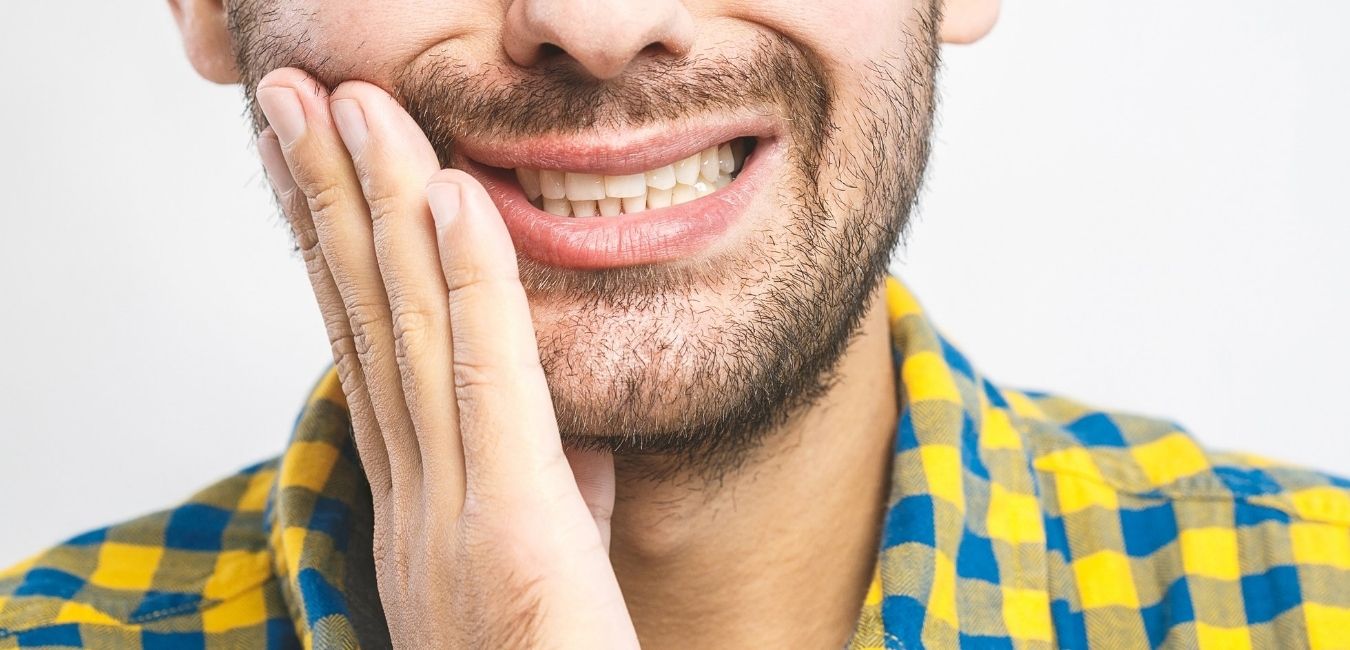

When the enamel layer of the tooth is increasingly eroded and the other two layers, the dentine and pulp, become exposed, pain and sensitivity are common symptoms. Dentists report that tooth erosion has become more frequent particularly among children, teenagers and young adults.
Tooth Erosion is not the same as tooth decay, although the two conditions can happen at the same time. Tooth decay (caries) occurs when bacteria in the mouth turn sugar into acid, which can damage the tooth. Poor oral hygiene and frequent consumption of sugar are the causes of tooth decay.
How To Care for your teeth:
- Immediately after consuming acidic food or drink rinse your mouth with water, milk or recommended mouth wash.
- Drinks a lot of fluids throughout the day and especially in-between meals.
- Avoid or restrict your intake of acidic foods and drinks.
- Drink acidic drinks through a straw, place the straw tip well behind your front teeth at about mid-tongue.
- Delay tooth brushing for at least 30 minutes after acid exposure to allow saliva to help stabilize the tooth enamel.
- Brush your teeth at least twice daily using a soft toothbrush and a non-abrasive fluoridated toothpaste.
Recommendations: After brushing, spit out the excess paste and do not rinse. If you prefer to rinse, then reapply a small amount of fresh toothpaste to the teeth so that the benefit of the fluoride remains on the teeth.
For more information
Call 07 3369 8300 or book online
Contact us today and make an appointment to see our Woolloongabba Dentist or Milton Dentist